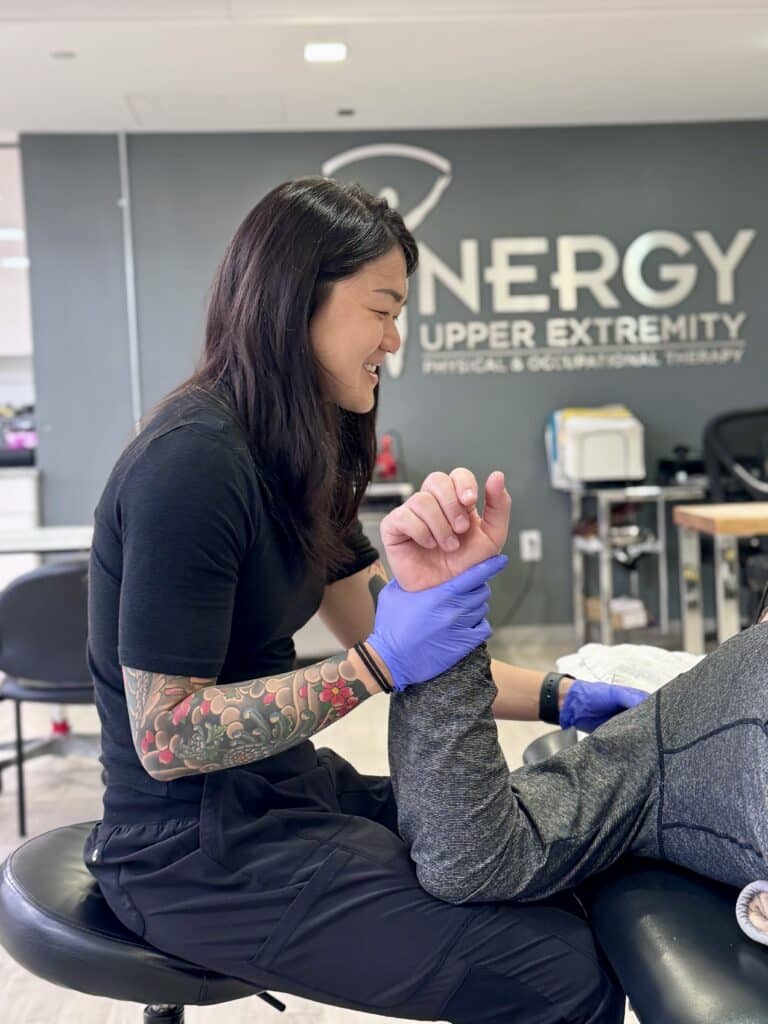
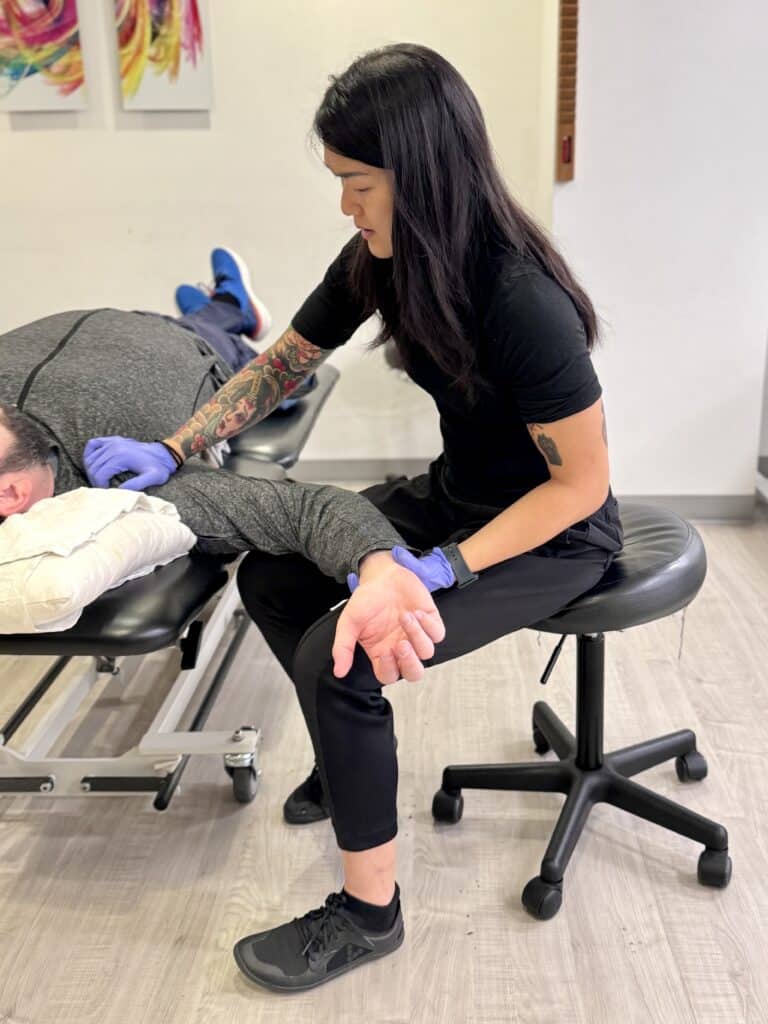
If you're dealing with frozen shoulder, rotator cuff injuries, impingement, or labral tears, Cynergy Physical Therapy offers expert care to reduce pain, improve mobility, and restore your shoulder function. Our highly trained therapists provide personalized treatment to help you regain strength and movement.
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis) Treatment
Frozen shoulder occurs when the shoulder capsule thickens and tightens, causing pain and limited motion. It progresses through four phases: freezing, frozen, thawing, and recovery.
Treatment:
- Early phase: Gentle stretching and soft tissue mobilization
- Later stages: Intensive exercises to regain range of motion and strength
Duration: Symptoms can last 15–24 months, but therapy helps speed recovery.
Postoperative Shoulder Care
After shoulder surgery (e.g., rotator cuff repair, labral repair, shoulder replacement), physical therapy is essential for regaining strength, flexibility, and function.
Goal: Return to daily activities and prevent re-injury through tailored rehabilitation.
Rotator Cuff Injury Treatment
Rotator cuff injuries can result from trauma or overuse, leading to pain, weakness, and difficulty with everyday movements.
Treatment: Focus on strengthening the rotator cuff muscles, improving posture, and enhancing movement patterns to alleviate pain and improve function.
Shoulder Impingement Treatment
Impingement occurs when the rotator cuff muscles or bursa rub against the shoulder blade, causing pain, weakness, and limited overhead movement.
Treatment: Stretching, strengthening, and improving posture to restore range of motion and reduce pain.
Labral Tear Shoulder Treatment
A labral tear can result from trauma or repetitive motion, causing pain, instability, and weakness in the shoulder.
Treatment: Mobilization, strengthening exercises, and stability training to restore movement and reduce symptoms.
Schedule a Consulation for Shoulder Pain
Call 888-462-0045 to book a consultation at our Midtown West, Midtown East, Chelsea, or Brooklyn locations.